A STUDY ON THE EFFECT OF WORKING CAPITAL ON THE PROFITABILITY OF INFOSYS
Sumathi A and Narasimhaiah T
VIT Department of Commerce, Karpagam University, India
DOI: 10.21917/ijms.2016.0047
Abstract :
The fixed and the current assets play a vital role in the success of any company. Managing the working capital is mandatory because, it has a huge significance on profitability and liquidity of the business concern. The increase in working capital helps in improving its liquidity. Thus, a company needs to have a correct balance between the liquidity position and the profits of the company. The various components for measuring the working capital management include the receivable days, Inventory turnover ratio, Payable days, Cash conversion cycle, Current ratio and Quick ratio on the Net operating profitability position of the Indian companies. The various factors like fixed assets on total assets, the Debt ratio and the size of the firm have also been used for measuring of the working capital management.
Keywords:
Profitability, Liquidity, Current Ratio and Quick Ratio, Working Capital
1. INTRODUCTION
Working capital is an effective tool for the measurement of both a company's effectiveness and its short-term financial position. Working capital is the difference between the current assets and current liabilities. In the field of financial affairs of companies, management of working capital is a very significant factor, which has a direct positive effect on profits of the firm as well as liquidity position of the company. Liquid position and the profits of the firm are two different sides of same coin. Optimum level of liquidity confirms a firm to meet their short term funds requirement and the optimum management of fund flow can be ensured by a profitable business. Liquid position shows the ability of company in meeting its short-term obligations. A firm has to aim at optimizing its liquid position and profits while conducting its daily business operations. Management of Working Capital contains greater balance of working capital factors like debtors, inventory and payables and the use of cash efficiently for day to day business activities.
Maintenance of optimum working capital balance is maintaining minimum working capital and realizing maximum possible returns. There is a greater relationship between profits of the firm and firm’s working capital. The capability of the company to earn profit can be considered as the ability of the company to maximize its profits. Profit is obtained by deducting expenditure from the revenue. Profits of a firm can be used as a measure of the financial performance of a company and the profit position is the guarantee for a company to remain working continuously in the world of business. Better Working capital management helps to make sure that the company has increased its profitability. Working capital management is important because of its significant effect on profits of company and thus the existence of company in the market. The ability of financial managers to manage their receivables, inventories, and payments has a greater effect on the stakeholders, success of the business and on profitability too.
The primary objective of any firm is to maximize their profits. But, maintaining the liquidity of the firm is also an essential objective. The problem is that growing profits at the cost of liquidity can bring major and effective problems to the firm. Therefore, there must be a proper balance between these two objectives or goals of the firms. One objective should not be met at cost of the other. If we do not care about profit, it becomes difficult to survive for a longer period. On the contrary if we do not care about liquidity, we may have to face the problem of insolvency or bankruptcy. For the above reasons management of working capital should be given proper importance and as it ultimately affect the profitability of the firm. Hence firms have to maintain an optimal level of working capital.
The goal of working capital management is to make sure that a firm is able to conduct its activities continuously and that it has ability to satisfy both meeting the short-term fund requirements and arising operational expenses. The working capital management involves maintaining inventories, accounts received and paid, and cash.
2. WORKING CAPITAL MANAGEMENT AT INFOSYS LIMITED
Infosys Limited is an Indian multinational corporation that provides various services like business consultancy, information technology, research, development, and software engineering and outsourcing services. It is headquartered in Bangalore, Karnataka. Infosys is the second-largest Indian IT services company by 2016 revenues, and the fifth largest employer of H-1B visa professionals in the United States of America in Financial year 2013. On 15 February 2015, its market capitalization was Rs. 263,735 crores, making it India's sixth largest publicly traded company. Infosys was co-founded in 1981 by CEO Narayan Murthy, Nandan Nilekani, N. S. Raghavan, S. Gopalakrishnan, S.D. Shibulal, K. Dinesh and Ashok Arora after they resigned from Patni Computer Systems. The company was incorporated as “Infosys Consultants Pvt Ltd.” with a capital of Rs.10,000 or US$1,250 (equivalent to about $3,254 in 2015) in Model Colony, Pune as the registered office. It got its first client, Data Basics Corporation, in New York. Company's corporate headquarters was relocated from Pune to Bangalore. On 15 January 2016, Infosys had 1,045 clients across 50 countries. Infosys has a global recognition with offices and development centres across the world. In 2012, Infosys announced a new office in Milwaukee, Wisconsin to service Harley-Davidson, being the 18th international office in the United States. Infosys hired 1,200 United States of America employees in 2011, and expanded the employee force by an additional 2,000 employees in 2012.
3. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Many previous research studies have indicated the relations between working capital management, liquidity, profitability, risk and many more factors of a company in different environments.
Rafuse [1] studied that suppliers were not interested in interest, rather they wanted their money. His more suggestions was that improvement of working capital by delaying payment to creditors was an inefficient and ultimately damaging practice, both to its practitioners and to the economy as a whole. He suggested that those seeking concentrated working capital reduction strategies should focus on stock reduction.
Eljelly [2] analyzed that liquidity management involves planning and controlling of current assets and current liabilities so that it can eliminate the risk of inability to meet short-term obligations and avoids much investment in these assets. Current ratio, regression analysis and correlation have been used to measure the result. The study found that the cash conversion cycle was of utmost important as a measure of liquidity than the current ratio that affects profitability. The size variable was found to have a major effect on profitability at the industry level. It was clear that there was an adverse relationship between profits of the firm and liquidity position indicators such as current ratio and cash gap in the Saudi sample examined.
Padach [3] analyzed that management practices are expected to assist managers in identifying zones where they might require improvement in the financial performance of their operation. The results provided owner-managers with information relating to the basic financial management practices used by their peers and their peers attitudes toward the selected practices. The working capital requirements of an organization change over times as does its internal cash generation rate.
Raheman and Naser [4] examined the working capital management and profitability position of Pakistani firms. An example of 94 Pakistani firms recognized on Karachi Stock Exchange for a period of 6 years from 1999 – 2004. The results indicated that there is an adverse relationship between variables of working capital management and profitability.
Solano et al [10] reviewed the effect of working capital management on SME profitability. To achieve the objective 8872 small to medium sized companies have been taken for the period over 1996-2002. Panel data methodology has been adopted and found that if cash conversion cycle will small it will help in improve the firm profitability. So, the managers of the firm should try to reduce their inventories and the number of days for which their accounts are outstanding.
Kaushik Chakraborty [5] checked the various studied done on management of working capital and its components. The studies related to working capital management as a whole would necessarily discuss the individual components of working capital and thus exclusive studies on individual factors of current assets and current liabilities were found to be very few. A deeper look into survey indicated that there were only a few studies available abroad and plentiful of studies in India. The survey also revealed that, though a few case studies on individual components automobile companies were present, there was no attempt in India to study the working capital management in any specific industry.
Dănuleţiu [6] Study the relation between the efficiency of the working capital management and profitability using Pearson correlation analyses and take a sample size of 20 annual financial records of companies covering period 2004-2008. The conclusion of the study is that there is a negative linear correlation between working capital management indicators and profitability rates.
Dong and Su [8] examined the relationship between profitability, cash conversion cycle and its components for listed firms in Vietnam Stock market. The results showed that there was a strong negative relationship between profitability and the cash conversion cycle. The time period was short in compare with some of the previous studies about the relationship between Management of working capital and profits of the firm.
Bhunia and Khan [7] analyzed the efficiency of Indian steel company by the effective management of liquidity. Data has been taken from 230 steel companies from CMIE database, over the period of 2002 to 2010. It was concluded that liquidity and profitable position is good and satisfactory of the company.
Patel and Parjapati [9] analyzed five steel companies to know the comparative position and uses of working capital. Various analyses such as ratio analysis and operating cycle analysis have been used. The study reveals that Tata steel ltd has the highest growth of net working capital maintenance during GRA - Global Research Analysis holding period followed by Jindal steel ltd. and it is negative with JSW steel. Net operating cycle of Jindal steel and Tata steel is adverse in each year that shows there is a greater working capital management in these companies.
4. STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
Working capital management of a firm is important for the following two reasons. An optimum part of the investment is invested in firm’s current assets
- a) Level of current assets will change quickly with thevariation in sales and
- b) The working capital management of a firm will have agreater impact on the firm’s profitability.
Hence, this study has been conducted to know effect of the size and rising of working capital and whether such an investment has grown or reduced over a period of time. After calculating the requirement of current assets, the important task of the financial manager has to choose appropriate source of finance in order to fund firm’s various current assets which helps in maximization of profits.
5. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
- To understand and analyse the relationship betweenManagement of working capital and Profits of the firm.
- To find out the effects of different components of workingcapital on the profits of the firm.
- To make suggestion for improvement for the successfulsurvival in the competition world.
6. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study was conducted on the financial data of Infosys Ltd. from the year 2011 to 2015.
6.1 COLLECTION OF DATA
This study is based on the secondary data collected from Infosys’s Annual Report, Balance Sheet, Financial Ratios and various other financial statements. Data is also extracted from different websites.
6.2 DATA PROCESSING
After the collection of data from various sources, the data has been classified into tables and analysis was conducted based on the classified data. An interpretation was drawn on the impact of working capital on firm’s profitability and analysis of ratios and Z score test are applied.
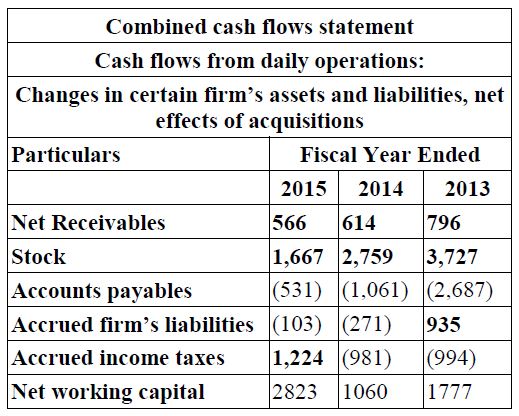
7. STATEMENT OF CHANGES IN WORKING CAPITAL OF INFOSYS LTD .
Working Capital determines the company's short term liquidity position or its ability to meet short term liabilities. It is termed as the difference between a company's current assets and current liabilities. Working Capital changes is recorded in the cash flow statement since it is one of the major ways in which net income can be different from firm’s operating cash flow. It is arrived at by adding the items that comes under the section Cash Flow Statement of the firm.
But by the year 2015, the working capital raised to Rs. 2823 (increased by Rs. 1763 compared to 2014) it depicts that the firm had adequate funds for their day to day operations and hence could maximize its profits in the respective year. Hence Infosys Company has volatility in its working capital structure. Thus for a firm to have a good conduct of business, it has to maintain adequacy in its working capital structure.
7.1 WORKING CAPITAL INVESTMENT EFFICIENCY TEST
7.1.1 Liquidity test:
Liquid or solvency position is a factor that signifies the capacity to meet the financial requirements as and when needed. The solvency ratios are used to measure the short term solvency position and indicate the capability of a firm to meet its fund requirements whenever they become due current liabilities are used as the indicator of the ratios because they are taken in order to represent the most emergency debt, that is retiring within one year or specifically within one operating cycle.
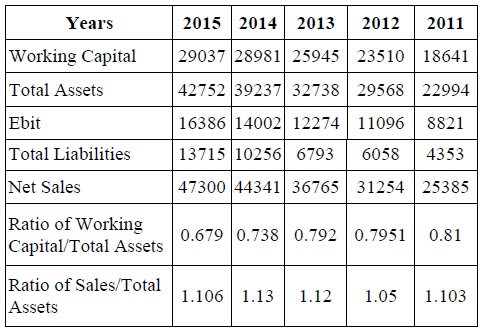
The current asset position of the company is presented above the table. It was 22994 in the year 2011, gradually increased to 29568 in the year 2012 after it was increased into 32738 and last year 2015 it was increased into 42752.
The liquid assets position was 5.28crores in the year 2011 and eventually reduced to 3.12 crores in the year 2015 and thus there should be a better management of assets by the company.
7.1.2 Solvency Test:
Rather than searching for a the best ratio, Prof. Edward Altman has established a new technique that takes into consideration the five key performance ratios combined into a single score called z-score which provides investors a better picture of a firm's financial health. This technique uses five ratios to determine both financial problems and operating crisis of the firms. He has used multiple decrement weight age analysis used for the different ratios. Such as,
- X1 = (Working capital/Total of firm’s Assets)
- 1.2 X2 = (Retained earnings/Total of firm’s Assets)
- 1.4 X3 = (EBIT/Total of firm’s Assets)
- 3.3 X4 = (Capital fund/Total firm’s Liabilities)
- 0.6 and X5 = (Sales/Total firm’s assets)
- 0.999
The final z-score is achieved by adding all the above i.e,
- 1) If the ‘z’ score is above 3.0 - the company is secured based on these financial data.
- 2) If the score lies between 2.7 and 2.99, this is the area where one should exercise caution.
- 3) If the score lies between 1.8 and 2.7 there are better chances of the company going insolvent within two years of operations from the data of financial data given.
- 4) If the ‘z’ score is below 1.8 - chance of financial embarrassment is very high
From the above data it can be determined that even the company has not at all reach the financially healthy position at any point of the time under this study. But from the achieved level of 1.103 in 2011 it reaches 1.05 in 2012 implies the recovery from the financial crisis and exercising of an effective turn around strategies. But it is not a progress. In the very next year it was increased to 1.12 but after that it started gradually but the last year it again went declined 1.106.
8. FINDINGS AND SUGGESTIONS
On the basis of key findings from this study it has been observed that the management of a firm can increase the value for their shareholders by decreasing the credit period allowed. The management can also create returns for their shareholders by adding more inventories to meet an optimum level. Firms can also take long to pay their creditors .Firms are capable of employing sustainable competitive advantage by way of effective and efficient usage of the resources of the firm by reducing the cash conversion cycle to its minimum. By doing so, the profits of the firms are expected to grow over a period of time.
Hence it is suggested that the computation of working capital should be done at an optimum level. This helps the firm to maintain its current assets and liabilities in a better way and so that more returns can be made available to the shareholders.
9. CONCLUSION
In this study, it is clear that the overall position of the working capital of Infosys is satisfactory, but there is a need for improvement in inventory. From the beginning stage of the company the working capital is not satisfactory. But now it has growing trend, a major portion of the current assets are maintained in the form of firm’s stock or inventory, on the other hand other current assets are properly utilized and maintained.
The firm’s liquidity or solvency position majorly depends upon the inventory size maintained but other factors like debtors, advances and loans, cash and bank balances, bills receivables etc. are also responsible. However, through this study it was founded that there is need for an immediate improvement in working capital and inventory. The management of Infosys must try to properly utilize the inventory and try to hold the required inventory, so that liquidity will not interrupt.
REFERENCES
[1] Maynard E. Rafuse, “Working Capital Management: An Urgent Need to Refocus”, Journal of Management Decision, Vol. 34, No. 2, pp. 59-63, 1996.
[2] Abuzar M.A. Eljelly, “Liquidity-Profitability Tradeoff: An Empirical Investigation in an Emerging Market”, International Journal of Commerce and Management, Vol. 14, No. 12, pp. 48-61, 2004.
[3] Kesseven Padach, “Trends in Working Capital Management and its Impact on Firms’ Performance: An Analysis of Mauritian Small Manufacturing Firms”, International Review of Business Research Papers, Vol. 2, No. 2, pp. 45-58, 2006.
[4] Abdul Raheman and Mohamed Nasr, “Working Capital Management and Profitability-Case of Pakistani Firms”, International Review of Business Research Papers, Vol. 3, No. 1, pp. 279-300, 2007.
[5] Kaushik Chakraborty, “Working Capital and Profitability: An Empirical Analysis of Their Relationship with Reference to Selected Companies in the Indian Pharmaceutical Industry”, The IUP Journal of Management Research, pp. 1-19, 2008.
[6] Adina Elena Danuletiu, “Working Capital Management and Profitability: A Case of Alba County Companies”, Annales Universitatis Apulensis Series Oeconomica, Vol. 1, No. 12, pp. 364-374, 2010.
[7] Amalendu Bhunia, Islamuddin Khan and Somnath MuKhuti, “A Study of Managing Liquidity”, Journal of Management Research, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 1-22, 2011.
[8] H.P. Dong and J.T. Su, “The Relationship between Working Capital Management and Profitability: A Vietnam Case”, International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, Vol. 49, pp. 59-67, 2010.
[9] Ritesh Jayantibhai Patel and Kalpesh Prajapati, “A Comparative Study on Working Capital Management of Selected Steel Companies of India”, Asian Journal of Research in Business Economics and Management, Vol. 2, No. 7, pp. 1-18, 2012.
[10] P.J. Garcia Teruel and P. Martinez Solano, “Effects of Working Capital Management on SME Profitability”, International Journal of Managerial Finance, Vol. 3, No. 2, pp. 164-177, 2007.